

Introduction
Location Map
Base Map
Database Schema
Conventions
GIS Analyses
Flowchart
GIS Concepts
Results
Conclusion
References
GIS Concepts
Raster data: Raster data consist of cells that are assigned values based on the attributes or fields that the user defines. The digital elevation model (DEM) we used is an example of raster data. Many of the analyses we ran required us to convert our base layers intop raster format. Output files were, then, rasters for these analyses. Raster data tend to resemble pixels when displayed:
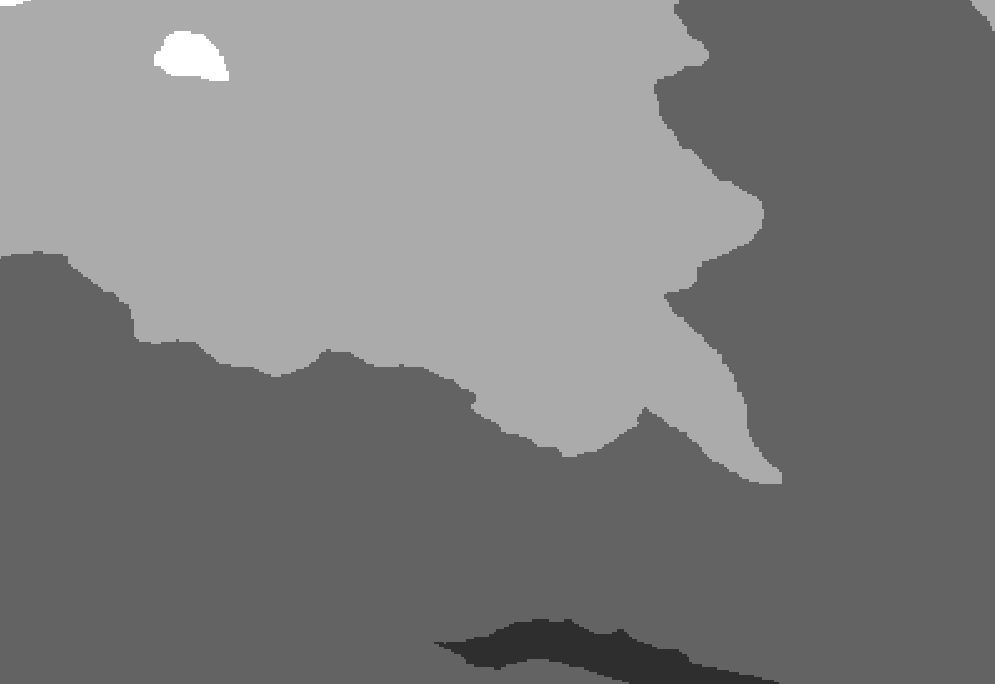
Raster Data: This image is from a zoomed-in region of our digital elevation model.
Vector data: Vector data are points, lines, and polygons. These shapes can represent just about any geographical feature one could imagine: lakes, roads, streams, and municipal boundaries are just a few. Outside of our DEM layer and the analysis result layers, all of our other basic files in the database are written with vector data.
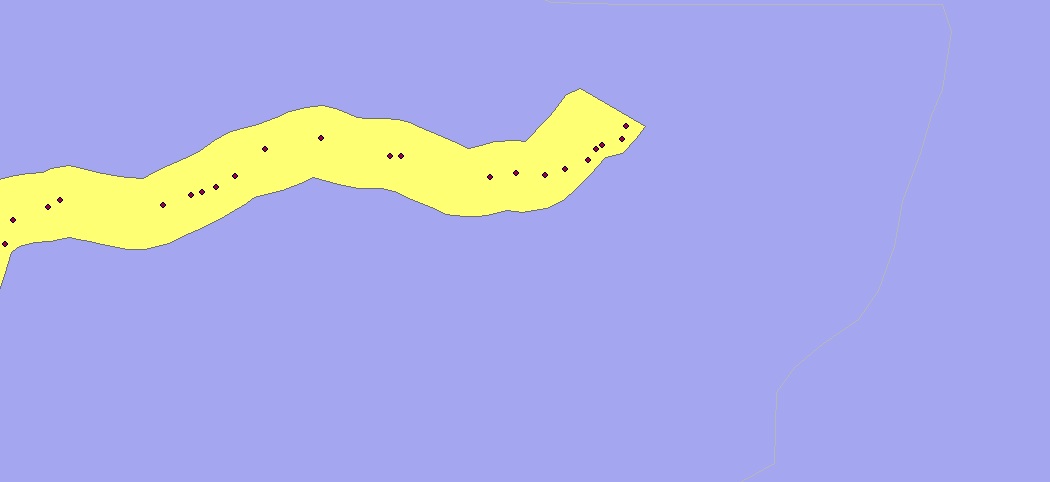
Vector Data: Our field sites are polygons (yellow) and the jams (small red dots) are point locations.
Cost-distance Modeling: Geographic information systems allow the user to measure distance in a variety of ways. Outputs can be obtained for Euclidean (straight-line) distance or a Weighted (cost) distance. We used cost-distance modeling in our examination of recreational access. This allowed us to model travel over roads from municipal areas to field site locations. For this analysis, two grids are needed-- the source grid (municipal areas and field sites, in our case) and the cost surface grid (raster road layer) (1).
Cluster Analysis: Spatial distribution can vary from one setting to another. In a basic sense, data points can be distributed randomly, evenly (or regularly), or in a clustered pattern. The Nearest Neighbor Index is one way of measuring the degree of spatial dispersion within data points. Neighborhood Analysis "measures the degree of spatial dispersion of features based on the minimum distance between individual (point and line) features. A scattered distribution has a greater average distance, while a clustered distribution has a smaller average distance" (2).
Citations
(1) M. Laituri. NR 505 Course Materials: Lab 12 Part A. Revised by R. Boone Fall 2010.
(2) D. Theobald. 2000. GIS Concepts and ArcView Methods. Third edition, Conservation Planning Technologies.