Introduction
Location Map
Base Map
Database Schema
Conventions
GIS Analyses
Flowchart
GIS Concepts
Results
Conclusion
References
![]()
GIS Concepts
GIS Concepts
Project in NAD_1983_UTM_Zone_13N
Coordinate systems allow geographic datasets to use common locations for integration of data. Our first step was to ensure that all of our data shared the same coordinate system in order to align spatial references. The North American Datum (NAD) 1983 is a common projected coordinate system which minimizes spatial distortion in our study area.

Image courtesy of Sonoma.edu
Mosaic
Due to how the National Map Viewer partitions its data, we had to download a number of different rasters to encompass our study area. We used the mosaic tool to connect multiple input rasters into a single raster.

Hillshade
Hillshades model the illumination of a surface by setting a position for a hypothetical light source and calculating the illumination values of each cell in relation to neighboring cells. We used this tool to better display the topography of our study area.

Clip
We used the clip tool to frame our study site and limit the scope of our interpolation analyses. The clip tool cuts out a piece of one feature class using one or more features in another feature class. We used it to remove excess areas of the DEM raster which we did not need for our interpolations.
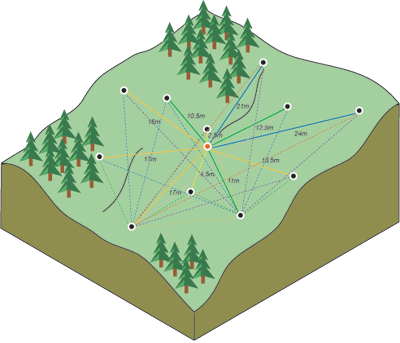
Inverse Distance Weighted (IDW) Interpolation
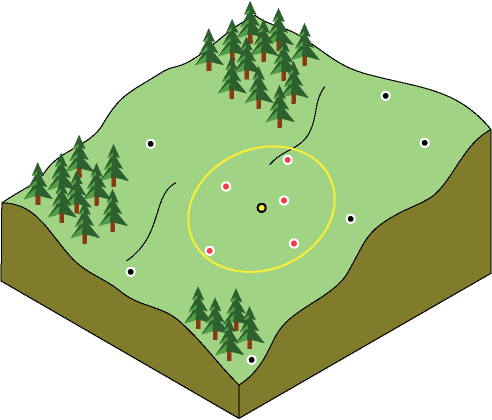
IDW interpolation assumes that things that are close to one another are more alike than those that are farther apart. To predict a value for locations like the ski resorts, IDW uses the measured values surrounding the prediction location. The measured values closest to the prediction location have more influence on the predicted value than those farther away. In the graphic below, the red points carry more weight on the value of the predicted (yellow) dot. This is a fairly simplistic interpolation technique, so we just used it as a starting point for our analysis.
Kriging
Kriging assumes that the distance or direction between sample points reflects a spatial correlation that can be used to explain variation in the surface. This is a geostatistical technique based on autocorrelation, the statistical relationships among the measured points. As the graphic below shows, this is a more involved process with multiple steps and more complicated mathematics than IDW.